autoclave chitosan|chitosan extractions : mail order With the recent progress in extraction methodologies and instrumentation sophistication, . Premium Quality Stone and Brick Over 25 Years of Industry Experience. Your premier Arizona Stone Supplier.
{plog:ftitle_list}
As we learned in our post about preventing the spread of infections in hospitals, the autoclave, also called a steam sterilizer, ensures the sterilization of medical instruments and materials used everyday in surgeries, procedures, and .
Mechanism of hydrogelation of chitosan-gluconic acid conjugate (CG) aqueous . Preparation of chitosan from Iraqi shrimp shell by autoclave, studying some .
This article presents a review on the applications of hydrothermally treated .
With the recent progress in extraction methodologies and instrumentation sophistication, . When autoclaved, urea hydrolyzes in an acidic chitosan aqueous solution, and .
Chitosan-based electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds have been selected as wound healing/tissue scaffolds because of their extracellular matrix nature and biocompatible properties. However, crosslinking of scaffolds is necessary to avoid lysozyme degradation in an aqueous environment, as a stable scaffold is crucial for the activities of fibroblasts, including adhesion . In addition to conventional methods (steam autoclave and gamma irradiation), a recent ozone-based method of sterilization was also tested. A model chitosan-tripolyphosphate (TPP) hydrogel nanoparticles (CS-HNP), .
natural polymer chitosan
In the present study, we examined the influence of autoclave sterilization (121°C, 20 min) on the characteristics of CG cryogel because complete sterilization was one of the fundamental requirements for medical devices. . Chitosan is a naturally-derived aminopolysaccharide composed of repeating units of d-glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine .
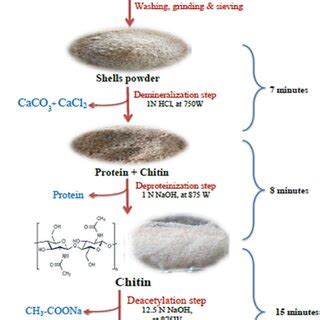
In the autoclave method, the chitin is treated with NaOH solution at elevated temperature and pressure in an autoclave. According to a recent report, the highest yield of chitosan is obtained with the autoclave method and the lowest observed with the microwave method (Sedaghat et al. 2017).Chitosan is obtained by hydrolysis of a chitin-rich extract. Chitin is a polysaccharide composed of several N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units interconnected by β (1.4) type linkages. . The medium is sterilised before use in an autoclave at 120 °C for 20 min. The Petri dishes are inoculated by pour plate method and spiral plating method. After .
Chitosan is made up of chitin via partial deacetylation with alkali. Rectify to Chitosan, a polycationic polymer is made up of chitin via partial deacetylation and has extensive biological applications because of its exclusive chemical nature, its positive charge, and the presence of reactive and hydroxyl groups.
Keywords: Chitosan; Polyamide66; Deacetylation; Polymer blends; Thermal properties; Morphological properties. . The use of an autoclave also led to a dramatic reduction in the time of deacetylation to just 30 minutes as compared to several hours when using the boiling method. Based on this result, only samples having a DD of more than 50% .
microwavable chitosan
The aim of this study was preparing chitosan from Iraqi shrimp shell by autoclaved chitin with concentrated sodium hydroxide (50%) at 121c°for15min.Some physiochemical characteristics and .
Chitosan (CS) is a linear polysaccharide biopolymer, one of the most abundant biowastes in the environment. This makes chitosan a potential material for a wide range of applications. . The two most common reactors used for the HTC process are pressurized Parr reactor and autoclave reactors. Autoclave reactors are usually stainless steel or . In the present study, we examined the influence of autoclave sterilization (121°C, 20 min) . Chitosan is a favored candidate to prepare hydrogel wound dressings due to its exceptional biological characteristics that can promote wound healing. Show abstract. Chitosan (CS) is a linear polysaccharide which is achieved by deacetylation of chitin .
Chitosan is known for its antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. However, chitosan possesses disadvantages, such as low mechanical and thermal stability and high moisture sensitivity, limiting its industrial applicability. . Preparation of chitosan from Iraqi shrimp shell by autoclave, studying some physiochemical properties and .Chitosan- β-glycerophosphate hydrogels have been researched and used in many studies. This study investigates the various factors that influence the gelation mechanism, such as gel formation rates, temperature, pH, time, and gel specificity. . If the hydrogel must be sterile, then autoclave all solutions separately at 121°C for 15 minutes .
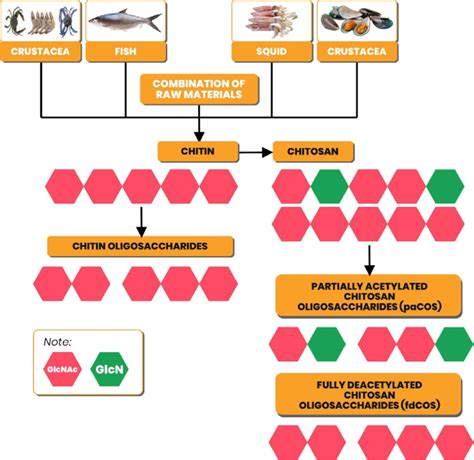
Conventionally, chitosan hydrogels are acidic and contain toxic chemicals because chitosan is soluble only in acidic solvents and requires toxic additives such as chemical crosslinkers and polymerization agents to fabricate chitosan hydrogels. These properties prevent chitosan hydrogels from being used for medical applications. In this study, chitosan hydrogels . Chitosan is obtained from chitin that in turn is recovered from marine crustacean wastes. The recovery methods and their varying types and the advantages of the recovery methods are briefly discussed. . chitosan extraction from marine crustaceans has also been achieved outside of chemical extraction through autoclave-based methods [36,37,38 .
The common polymer material used as a trapping matrix for encapsulation is chitosan (Andikop utri et al. 2021), which is a natural polymer compound ob tained from insect exoskeleton (Baharlouei . Natural polymers such as chitosan are of great attention in medicine and biotechnology [1].Chitosan have shown exceptional properties including biocompatibility, biodegradability, nontoxicity, antimicrobial activity, low immunogenicity, inexpensiveness and accessibility [2].It is a multifunctional and eco-friendly antifouling compound [3] which is known . numerous inter- and intramolecular hydrogen bonds [14]. Chitosan has a similar crystalline structure [14] and CG, a polymer of chitosan partly modified with gluconic acid, also retains a chitosan’s crystalline structure. Therefore, CG was expected to form hydrogels with the crystalline portion of CG as the crosslinking point. Chitosan has drawn tremendous interest in both academic and industrial fields due to its non-toxicity, antibacterial activity, biodegradability and high biocompatibility. . the wet alcogels were placed in an autoclave that was filled with ethanol. The pressure of autoclave system was tardily increased up to 5 MPa in 30 min by introducing CO 2 .
extracting chitosan from raw material
For instance, Takei et al., investigated how autoclave treatment affected cryogels made of physically crosslinked chitosan-gluconic acid for use as wound dressings [11]. They demonstrated that the .Chitosan extraction has been achieved by microwave heating and compared with that of conducting the deacetylation in an autoclave. High molecular weight chitosan (as determined by viscosity measurements of chitosan in dilute acetic acid solution), white color, high water binding capacity (WBC) and fat binding capacity (FBC) has been obtained by .
Chitosan from African giant snail (Achatina fulica) shells derived through autoclave- (SSC A) or ultrasound-assisted (SSC U) deacetylation was characterised and evaluated for quality and shelf life of tomatoes and cucumbers over 10 days of ambient (26 ± 2 °C) and refrigerated (4 ± 2 °C) storage.A 64.03 and 54.41% deacetylation degrees were achieved for .Chitosan, a biopolysaccharide having structural characteristics similar to glycosaminoglycans, seems to be an ideal non-toxic and bioabsorbable biopolymer. This study highlights the effects of some physical and chemical methods of sterilization on chitosan films, .Chitosan presents interesting characteristics, e.g. biocompatibility, low toxicity, biodegrad-ability, antimicrobial activity and low immunogenicity, which make it a promising material . steam autoclave and an innovative ozone treatment. The effects of sterilization were assessed through an extensive characterization of the materials, before and This review discusses five strategies for fabricating porous chitosan materials, i.e., cryogelation, freeze-drying, sol-gel, phase inversion, and extraction of a porogen agent. Each approach is described in detail with examples related to the preparation of chitosan materials. . Then, the gel was placed in an autoclave and encapsulated in a .
Chitosan from African giant snail (Achatina fulica) shells derived through autoclave- (SSCA) or ultrasound-assisted (SSCU) deacetylation was characterised and evaluated for quality and shelf life .Chitosan from African giant snail (Achatina fulica) shells derived through autoclave- (SSC A) or ultrasound-assisted (SSC U) deacetylation was characterised and evaluated for quality and shelf life of tomatoes and cucumbers over 10 days of ambient (26 ± 2 °C) and refrigerated (4 ± 2 °C) storage.A 64.03 and 54.41% deacetylation degrees were achieved for SSC A and SSC U, .Steam sterilizers (also referred to as autoclaves) are an essential part of the decontamination and sterilization process performed by sterile processing departments (SPD) in healthcare facilities. STERIS offers one of the broadest range of steam sterilizers and has a solution available to maximize department productivity and optimize workflow.
diy home autoclave
diy non autoclave aircrete panels
$17.99
autoclave chitosan|chitosan extractions